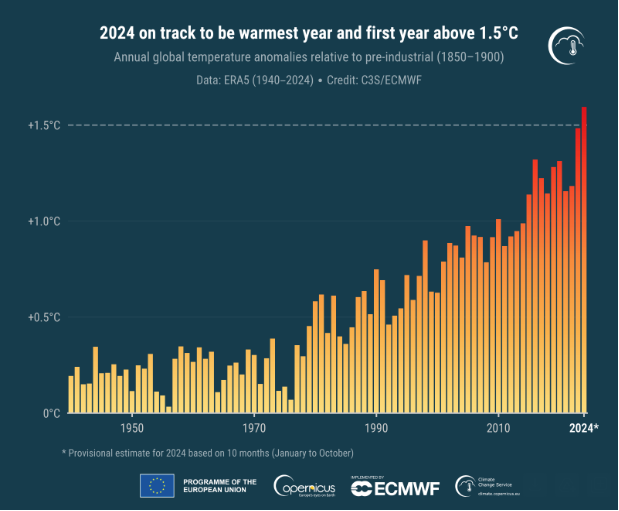
Local weather scientists working on the European Union’s Copernicus Local weather Change Service have introduced that 2024 is “nearly sure” to be the warmest yr on file.
In accordance with its ERA5 dataset, the company stated it was “nearly sure” that the annual temperature for 2024 will probably be greater than 1.5 levels Celsius above the pre-industrial degree, and it’ll probably be greater than 1.55 C above.
For many years, scientists have warned that common world temperatures shouldn’t get any increased than 1.5 C above pre-industrial occasions as a way to forestall lethal climate situations that would influence folks worldwide.
The world has already warmed significantly and has seen the results with back-to-back warmth waves, droughts and unprecedented flooding and hurricane occasions. The best way farmers are in a position to develop meals has already began to shift, and with 1.5 to 2 levels Celsius of warming, agricultural yields will decline and sea ranges might rise as much as 10 toes, researchers have discovered. Consultants say the oceans will even be hotter, fueling extra highly effective hurricanes and threatening ecosystems which can be elementary for economies and assist shield areas from inclement climate.
Copernicus Local weather Change Service /ECMWF
“This marks a brand new milestone in world temperature data and may function a catalyst to boost ambition for the upcoming Local weather Change Convention, COP29,” stated Samantha Burgess, deputy director of the Copernicus Local weather Change Service, in an announcement.
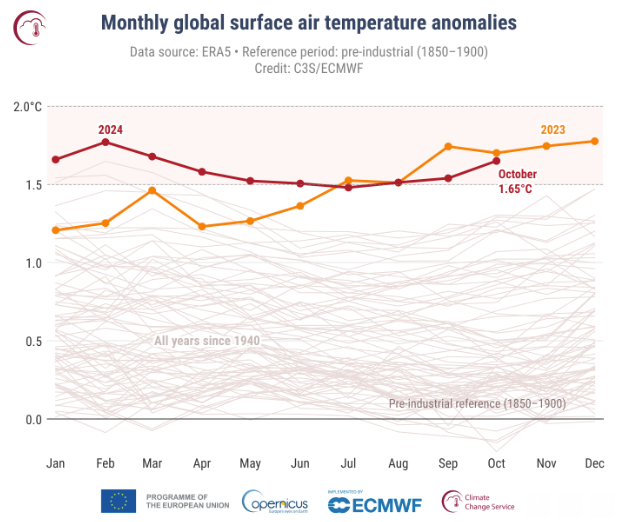
The Copernicus Local weather Change Service stated the typical world temperature anomaly for the primary 10 months of 2024 (January to October) is 0.71 C above the 1991-2020 common, which is the best on file for this era and 0.16 C hotter than the identical interval in 2023.
“The typical temperature anomaly for the remainder of 2024 must drop to nearly zero for 2024 to not be the warmest yr,” the company stated.
The company added that provided that 2023 was 1.48°C above the pre-industrial degree in accordance with its ERA5 mannequin, it was additionally probably that the annual temperature for 2024 will probably be greater than 1.55°C above.
European temperatures had been above common over nearly the entire continent, Copernicus discovered. Exterior Europe, temperatures had been most above common over northern Canada, and well-above common over the central and western United States, northern Tibet, Japan and Australia.
Copernicus Local weather Change Service /ECMWF
The company additionally stated Arctic sea ice reached its fourth lowest month-to-month extent for October, at 19% beneath common. Sea ice extent is a measure of the floor space of the ocean which is roofed by ice.
Sea ice focus anomalies had been effectively beneath common in all peripheral seas of the Arctic Ocean, notably within the Barents Sea, Canadian Archipelago, and north of Svalbard, the company stated.
Antarctic sea ice extent was 8% beneath common in October, which was the second-lowest such common behind solely October 2023, when it was 11% beneath common, Copernicus stated. These numbers continued “a sequence of huge adverse anomalies noticed all through 2023 and 2024.”
The Copernicus Local weather Change Service, which is funded by the EU, routinely publishes month-to-month local weather bulletins reporting on adjustments noticed in world floor air and sea temperatures, sea ice cowl and hydrological variables. All of the reported findings are primarily based on computer-generated analyses and the ERA5 dataset, which makes use of billions of measurements from satellites, ships, plane and climate stations world wide.
In a report revealed final month, the United Nations warned that the world is now in “local weather crunch time” as greenhouse gases — which lure warmth within the ambiance that warms world temperatures and fuels extra excessive climate occasions — have hit “unprecedented ranges.”
“The numbers paint a transparent image,” the U.N. stated. “To maintain emissions beneath the vital 1.5-degree goal set in Paris in 2015, nations should lower emissions by 42 % general by 2030 and obtain a 57 % discount by 2035.”